Determining the Rate Law from Experimental Data.
Determining the Rate Law from Experimental Data. In order to experimentally determine a rate law, a series of experiments must be performed with various starting concentrations of reactants. The initial rate law is then measured for each of the reactions. Consider the reaction between nitrogen monoxide gas and hydrogen gas to form nitrogen gas.
Rate Laws from Rate Versus Concentration Data (Differential Rate Laws) A differential rate law is an equation of the form. In order to determine a rate law we need to find the values of the exponents n, m, and p, and the value of the rate constant, k.

Chemical Kinetics Chemical kinetics is the study of the speed at which chemical and physical processes take place. In a chemical reaction it is the amount of product that forms in a given interval of time or it can be defined as the amount of reactant that disappears in a given interval of time.

Rate Law for Reversible Reactions Example: Write the rate law for the elementary reaction Here k fA and k rA are the forward and reverse specific reaction rates both defined with respect to A. (1) (2) At equilibrium The equilibrium constant decreases as T increases (exothermic rxns) K e increases as T increases (endothermic rxns).

Differential rate equations can be used to calculate the instantaneous rate of a reaction, which is the reaction rate under a very small time interval. It can be noted that the ordinary rate law is a differential rate equation since it offers insight into the instantaneous rate of the reaction. Integrated Rate Equations.
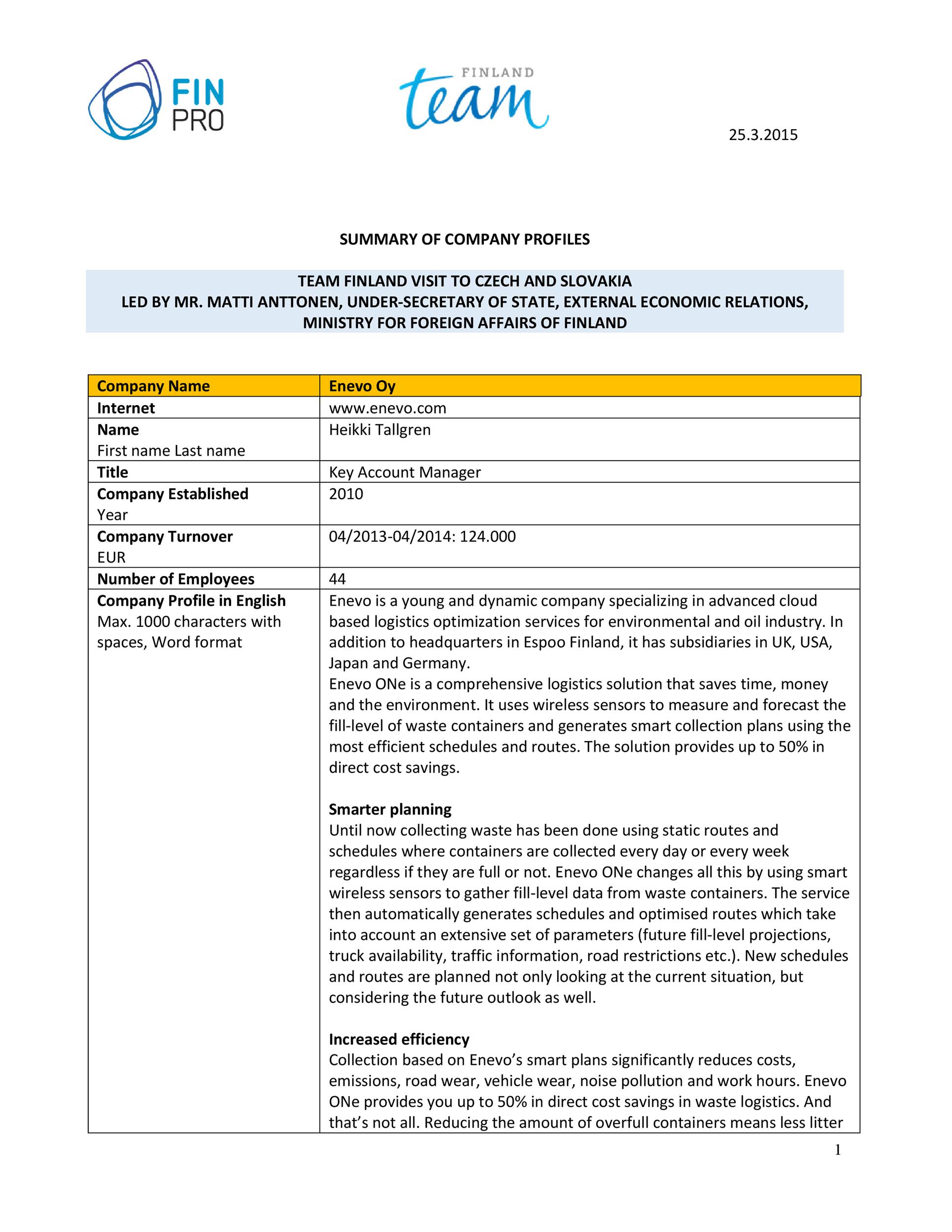
We can use this data to help us figure out x and y and write a rate law equation for this reaction. In order to find x, we need to look at the data and determine what happens to NO when H 2.

Use this information to write a rate law for this reaction, and calculate the value of the rate constant, 'k.' Round your value for the rate constant to 2 significant digits.

Rate equations. Measuring a rate of reaction. There are several simple ways of measuring a reaction rate. For example, if a gas was being given off during a reaction, you could take some measurements and work out the volume being given off per second at any particular time during the reaction.

Rate Laws from Graphs of Concentration Versus Time (Integrated Rate Laws) In order to determine the rate law for a reaction from a set of data consisting of concentration (or the values of some function of concentration) versus time, make three graphs. (A) versus t (linear for a zero order reaction) ln (A) versus t (linear for a 1 st order.
Determining the Rate Law from Pressure Data Problem 14-80 The decomposition of ethylene oxide at 690 K is monitored by measuring the total gas pressure as a function of time.

Explanation:. When determining the rate law for a reaction, you need to determine the order for each reactant in the reaction. This can only be accomplished by performing an experiment where different trials show how the initial reaction rate changes based on the initial concentrations of the reactants.
EXPERIMENT 6: RATE LAW OF AN IODINE CLOCK REACTION 63 where y is the only unknown in the equation. Solve for y by finding the antilog of both sides of the equation. A similar operation can be done by keeping the bisulfite concentration constant in order to solve for x.

Using Rate Law Tutorial Key Concepts. Reaction rate is the time rate of change of concentration of a reactant or product in a chemical reaction. The rate of consumption of a reactant is always negative. The rate of formation of a product is always positive.